Foreword
Dear readers,
It is my pleasure to bring to you the latest edition of our newsletter.
In this edition, we delve into the transformative impact of generative AI (GenAI) in digital payments, by providing you with a comprehensive understanding of the opportunities and challenges related to the adoption of generative AI. We also touch upon the intricacies of this dynamic and evolving field.
I hope you find this newsletter to be a useful and insightful read.
For further details or feedback, please write to: vivek.belgavi@pwc.com or mihir.gandhi@pwc.com
Introduction
GenAI has emerged as one of the most discussed technologies in 2024, attracting significant interest of technology leaders in financial institutions across the world. In addition to its ability to generate new content, it is also finding applications in other areas. In this newsletter, we discuss and understand the role of GenAI in the digital payments industry.
Understanding GenAI
GenAI is a subset of artificial intelligence, which is focused on creating new content – including text, images, audio or video – which mimics humangenerated data. Unlike traditional AI systems that are typically task-oriented and rely on predefined rules or patterns, GenAI models have the ability to generate new content based on the patterns and structures they learn from large datasets with the help of machine learning (ML).
Some of the key features of GenAI are as below:
- Ability to create new content, image, audio and video
- Contextual understanding of the input data or environment
- Increased accuracy due to the ability to process and comprehend large volumes of high-quality data
Evolution of GenAI
The evolution of GenAI is marked by significant milestones in the field of mathematics, statistics, ML and AI.
- Contribution of mathematics and statistics: The groundwork for GenAI’s evolution was laid by advancements in mathematics and statistics. Concepts such as linear algebra, calculus, probability theory and optimisation algorithms played a key role in developing the framework in order to better understand data and building models. Statistical methods played a crucial role in analysing patterns and making predictions, which formed the basis for early ML algorithms.

- Transitioning from ML to AI: ML gained prominence during the rapid emergence and evolution of GenAI. Initially, ML algorithms were developed to process data and make predictions, which were often based on mathematical models. As ML techniques advanced, they became adept in handling more complex tasks such as image processing and natural language processing (NLP). Image processing algorithms enabled computers to interpret and analyse visual data, while NLP algorithms allowed them to understand and generate responses that can easily be interpreted by a human.
- Advanced training with large datasets: One of the key turning points in the evolution of GenAI was the capability of systems to process and understand large-scale datasets because of the increase in computational power. Access to vast amounts of data enabled researchers to train more sophisticated models in order to capture intricate patterns and nuances in various domains. This led to the rise of large language models (LLMs), such as GenAI, which could generate human-like text and perform a wide range of language-related tasks with remarkable accuracy.
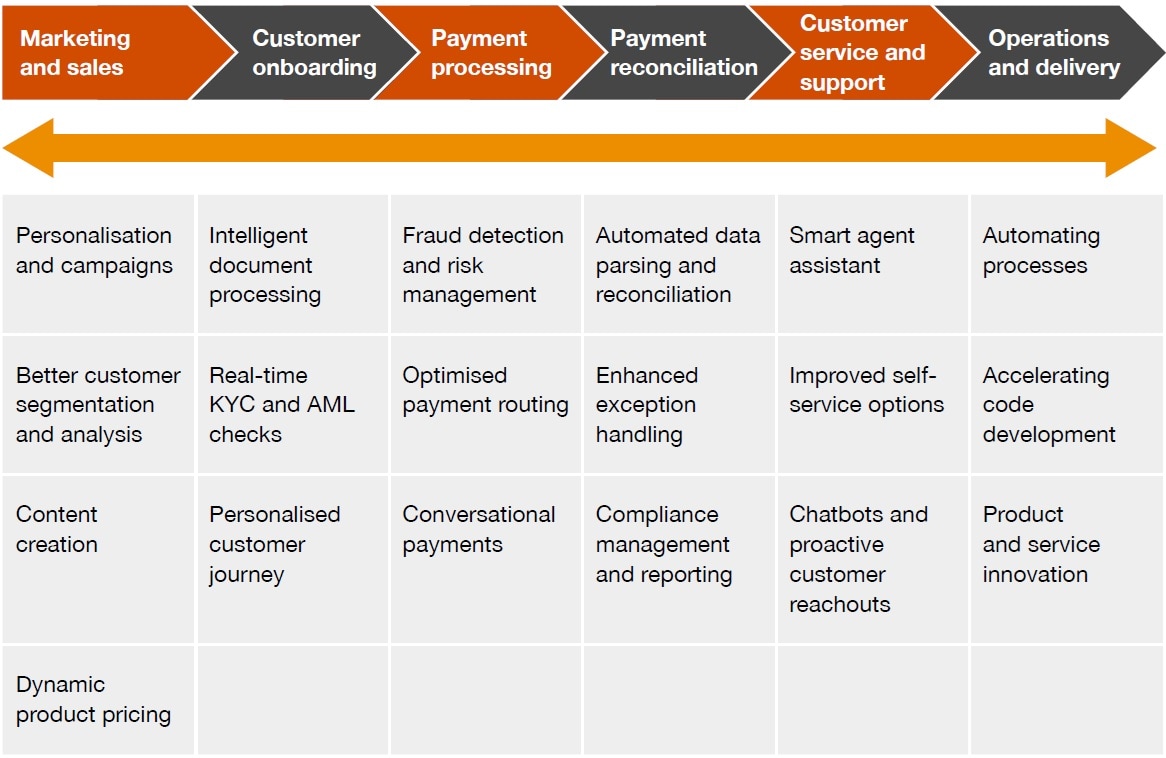
GenAI can have diverse applications in various domains, ranging from marketing and sales to operations and analytics. In the next section, we highlight some of these applications in the payments domain.
Applications of GenAI in payments
GenAI has the potential to revolutionise payments with a multifaceted approach, by boosting personalisation and security and increasing the efficiency of digital payments, thus benefiting both businesses and consumers alike.
It could potentially provide foolproof solutions to address the entire payments lifecycle from marketing and sales, customer onboarding, know-your-customer (KYC), to customer service and risk management.
Some of the key applications of GenAI in the payments domain are highlighted below.
Personalisation, customer segmentation and campaigns
GenAI models can analyse transaction histories and customer preferences to generate recommendations for personalised products, services or payment options. This enhances customer experience as it provides patrons with tailored suggestions and ease in transactions, thus increasing customer loyalty. It can also help with dynamic content creation, which is specific to the customer.
Content creation
GenAI can improve marketing and sales effectiveness by helping create targeted content that can be leveraged to enhance outbound customer communications. Moreover, the images and content can be customised as per customer categories. For instance, a younger demographic can be made aware about specific offerings by promoting the same using relatable and eye-catching content.
Dynamic product pricing
GenAI models can analyse market dynamics, customer behaviour and inventory data to generate dynamic pricing strategies for products and services. This will enable banks and FinTechs to optimise real-time pricing based on demand, supply and other relevant factors.
Banks, FinTechs and insurance providers can leverage dynamic pricing models for products like loans, insurance premiums and investment portfolios. These models adjust pricing based on risk assessments, market conditions and customer preferences.
GenAI can be used to handle customer onboarding from the very first interaction through intelligent and automated identity verification solutions while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements to enhance efficiency and accuracy. Furthermore, it can facilitate the onboarding process by intelligent document processing and performing real-time KYC/ anti-money laundering (AML) checks with customer onboarding documents.
With GenAI, systems can adapt according to consumer preferences and recommend personalised customer journeys to enhance overall experience.
Example: An American multinational payment card service has implemented a GenAI system that analyses regulatory documents and provides recommendations to ensure compliance with AML and KYC regulations across multiple regions.
Customers initiate payments via different payment channels. With new channels emerging every day, it is paramount to streamline and secure these channels.
Some of the use cases of GenAI in payment \processing have been detailed below:
Conversational payments
GenAI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants facilitate conversational payments, enabling users to make transactions, check balances and receive support through natural language interactions. This is an important value-added service to attract customers and helps with the ease of making payments.
Fraud detection and risk management
GenAI can be used to develop dynamic risk-scoring models that assess the risks associated with payment transactions in real time. These models can assign risk scores based on various factors such as transaction amount, frequency, location and user behaviour, enabling the formulation of more targeted risk management strategies. GenAI models learn typical payment patterns and create synthetic examples of fraud, aiding anomaly detection systems. They also analyse transactional data and market trends to pre-empt risks, bolstering risk management and curbing financial fraud. This ensures that the payment is processed without fraudulent activity or money laundering.
Example: A Nordic-Baltic banking group has used the generative adversarial network (GAN) model to detect fraudulent transactions, resulting in a reduction in false positives.
Automating processes
Payment processes involve a significant number of middle-office activities – most of which are quite complex and require some amount of client interactions. GenAI can carry out and/or automate tasks like commercial contracts, requests for proposals, account plans, etc. GenAI can also be used to automate recurrent activities and streamline delivery.
Accelerated code development
Many traditional companies continue to have a strong dependency on legacy systems. GenAI can assist in facilitating bug detection, repairing code and performing user acceptance testing. GenAI can also be used to analyse existing codebases and libraries to recommend alternative solutions or approaches.
Product and service innovation
GenAI not only fastens delivery timelines by letting teams focus on important activities but also assists them in developing new product and service designs with the help of its computational and documentation capabilities.
Example: One of the largest private banks in India is rolling out its LLM-powered website in 2024. The bank also plans a private LLM to write credit assessments and business requirement documents.
Automated data parsing and reconciliation
GenAI is a powerful tool for automatic data parsing and is especially used for unstructured data. Use of GenAI to parse data helps in increasing accuracy and minimising errors. Moreover, it can extract relevant information from invoices, receipts and bank statements – regardless of the format.
GenAI can provide valuable insights into payment patterns and help businesses optimise reconciliation.
Enhanced exception handling
GenAI can analyse exceptions to find root causes and recommend automatic suggestions for alternative approaches when the same exception repeats. However, this use case is still evolving but has the potential to be used widely.
Compliance management and reporting
NLP models in GenAI models can be used to analyse regulations and compliance documents and automate recurring activities in payment workflows – e.g. conducting regulatory checks. This can ensure that the bank understands and follows the compliances required and the changes proposed. The reporting process can also be automated using enhanced pattern matching, with minimal or no human intervention.
Smart agent assistant
GenAI can provide real-time suggestions and knowledge repository access to customer service agents, thereby improving human agents. They can also be used to draft personalised communications messages to customers.
Improved self-service options
GenAI can be used to create clear and concise information and personalise FAQs based on user behaviour and past interactions. It can also be used to develop interactive tutorials and guides that can help customers resolve queries on their own.
Chatbots and proactive customer reach-outs
GenAI can power chatbots and virtual assistants that assist users with payment-related inquiries, provide customer support and facilitate transactions through NLP.
Both GenAI and AI chatbots, despite using the same technology, serve different purposes. The content creation capabilities of GenAI can be used to personalise information and content for service agents. On the other hand, AI chatbots are designed to simulate conversations directly with the users through text or voice messages.
Examples:
- A leading commercial bank in the UK has recently announced the use of GenAI by making enhancements to its existing virtual assistant. This is expected to provide customers with access to a wider range of information through conversational interactions.
- India’s leading payment infrastructure innovator has implemented a GenAI-powered chatbot aimed at enhancing awareness of digital payment products and helping customers with their grievances.
Handling risks
While the adoption of GenAI in the payments domain offers significant benefits in terms of fraud detection, personalised user experiences and operational efficiency, it also poses inherent risks related to data privacy, bias, transparency and security.
Some of the key risks of GenAI include:
- Risks associated with GenAI powered recommendations
- Risks associated with real-time monitoring
- Risks of bias perpetuation in GenAI
Risks associated with GenAI powered recommendations
While personalised recommendations in banking aim to enhance the overall user experience, implementing them can lead to critical issues such as privacy concerns, algorithmic biases, and the necessity for transparency and fairness in recommendation algorithms.
Important considerations, especially the ones related to sanctions screening, fraud detection or exception handling, may require human intervention and expertise.
Risks associated with real-time monitoring
Real-time monitoring involves continuously tracking financial activities, transactions and data. It can bolster cybersecurity measures and fraud detection. The accuracy of suggestions provided by using LLMs needs to be validated as solely relying on GenAI suggestions might be risky.
In addition, as activities are tracked, this may result in privacy concerns as sensitive customer information is processed. Furthermore, balancing real-time responsiveness while minimising false positives poses another significant challenge.
For example, real-time monitoring may result in delay in processing payment transactions. This may affect the SLAs within which the payment transactions need to be processed.
Risks of bias perpetuation in GenAI
GenAI relies on historical data to make predictions and decisions. If the training data used to develop these systems is biased, either due to historical societal biases or data collection methods, the resulting algorithms may perpetuate or even amplify these biases. This could lead to the inadvertent perpetuation of biases in GenAI algorithms, resulting in unfair treatment of certain groups of users.
GenAI technologies have significant potential but should be implemented with caution. In the next section, we discuss how to unveil opportunities while navigating the challenges and risks ahead in order to accelerate FinTech innovation with GenAI.
Drivers for adoption
The implementation of GenAI is very capital-intensive and requires organisations to deal with a transition period that may disrupt the workflow, standard operating procedures and roles within them. The drivers of GenAI in payments are focused on making payments more efficient, secure, customercentric, and innovative.
Domain readiness refers to how prepared the industry is to adopt GenAI. The payments domain seems to be ready to transition to GenAI-integrated systems as it moves towards adopting new-age technologies and supportive infrastructure.
The demand for convenience in payments is a major driving force – not just for the adoption of GenAI but also the payments industry in general. The digital age has increased the need for on-demand services, which also includes payments. Convenience is key to any service irrespective of the domain, and the capabilities of GenAI only make its adoption even more logical in the payments industry.
Furthermore, data and quality remain essential drivers to accelerate the growth of the payments industry. The industry generates massive amounts of data pertaining to transactions, customer behaviour and finance. The introduction of ISO20022 will make more structured data available. This will make it easier to integrate GenAI solutions into existing systems.
The challenges and solutions for various drivers are illustrated below.
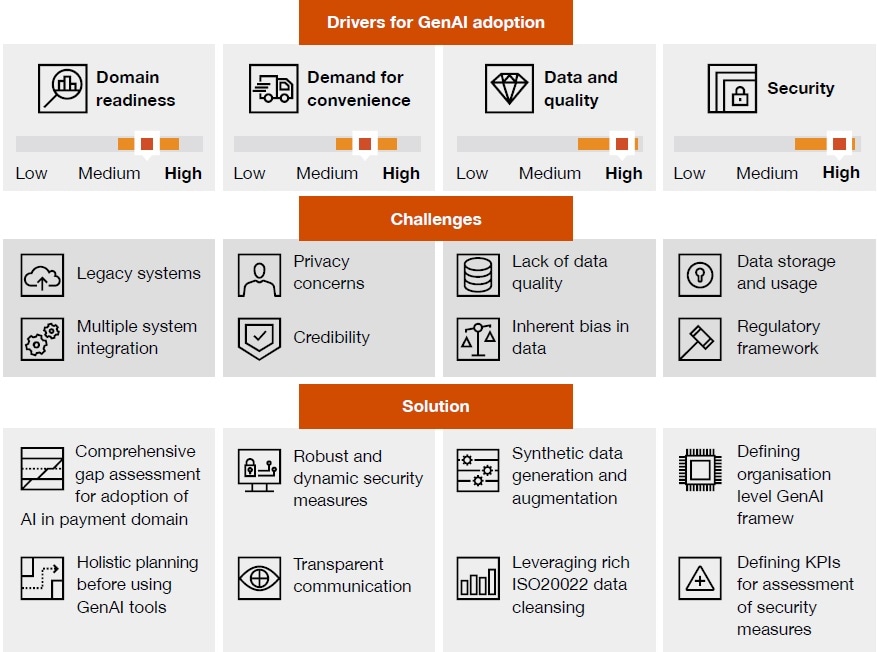
Security is paramount in the payments industry, especially since new and innovative payment channels are on the rise. GenAI’s ability to generate synthetic data, manage risks and fraud helps organisations to achieve their goals and maintain security standards.
Although organisations see GenAI as a solution to increase productivity and streamline operations, they must also deal with the risk of some jobs becoming obsolete and resulting in layoffs due to the adoption of these technologies. Organisations must therefore take steps to train employees and also have transparent communication on how GenAI would aid in productivity and not replace employees.
Overall, the successful adoption of GenAI in digital payments requires a comprehensive approach that addresses these challenges while leveraging the transformative potential of AI technology.
Conclusion
Considering the huge potential of the application of GenAI in the payments domain, it is clear that the digital payments landscape will undergo a major transformative shift. As the technology matures, further use cases would arise, making processes more automated and efficient. It is expected that the regulatory landscape will focus on the balance of power between innovation, consumer protection and responsible development of GenAI use cases. It will thus be important for financial institutions to revisit past implementations of older AI innovations like robot advisory and personal financial management tools that have not garnered the anticipated level of interest, uptake or results.
In our view, we have only scratched the surface when it comes to leveraging the power of GenAI in digital payments. Therefore, organisations need to proactively adopt the technology to harness its capability while also considering the security risks associated with it to achieve remarkable results.
By harnessing the power of AI, businesses and financial institutions can enhance efficiency, security and user experience across various payment channels – from personalised recommendations to proactive fraud detection. GenAI enables the development of innovative solutions that cater to the diverse needs of both consumers and businesses alike.
GenAI-driven solutions like fraud detection, risk management and customer service automation can help the Indian payment ecosystem to mitigate risks, improve operational effectiveness, and build trust among consumers.
Successful implementation of GenAI in digital payments requires collaboration among industry stakeholders, regulators and technology providers, to address challenges related to data privacy, security and regulatory compliance. By nurturing an ecosystem of innovation and collaboration, India can leverage GenAI to accelerate its journey towards a cashless economy, driving economic growth, and empowering millions of people with convenient, secure and inclusive digital payment solutions.
Sources
RETAIL-PAYMENTS-STATISTICS-2023Q1
https://pib.gov.in/ErrorPage.html?aspxerrorpath=/PressReleasePage.aspx
https://egazette.gov.in/(S(ijbwsz1wm4ooiuidgfgqmxf3))/SearchText.aspx?id=888848
NPCI retail payments statistics
Introducing UPI LITE: Making transactions Faster ➟ Secure ➟ Seamless
UPI 123PAY Partner Banks, Voice Service Providers and Solutions Provided
Author
Neha Dharurkar and Jai Kiran Kumar
About PwC
At PwC, our purpose is to build trust in society and solve important problems. We’re a network of firms in 151 countries with over 360,000 people who are committed to delivering quality in assurance, advisory and tax services. Find out more and tell us what matters to you by visiting us at www.pwc.com.
PwC refers to the PwC network and/or one or more of its member firms, each of which is a separate legal entity. Please see www.pwc.com/structure for further details.
© 2024 PwC. All rights reserved.