Role of emerging technologies and strategic partnerships for NBFCs
Non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) have played a pivotal role in meeting the financial needs of individuals and business that have traditionally remained un-served or underserved by banks. But the regulations for NBFCs have become stricter in recent times, the cost of borrowing has increased and NBFCs are focusing on niche markets and personalised products and services. NBFCs are now more focused on developing innovative products and catering to low-income, urban customers in unorganised sectors. In such a scenario, NBFCs are adopting business and operational models powered by technologies that seamlessly facilitate the design, launch, implementation and execution of tailored products and services. Investing in new technologies and strategic partnerships with incumbent financial institutions and FinTechs also allows NBFCs to lower their costs when it comes to increasing their customer base, lowering customer acquisition costs, servicing existing customers or de-risking the portfolio while trying to overcome the increasing formal credit penetration in a growing economy.
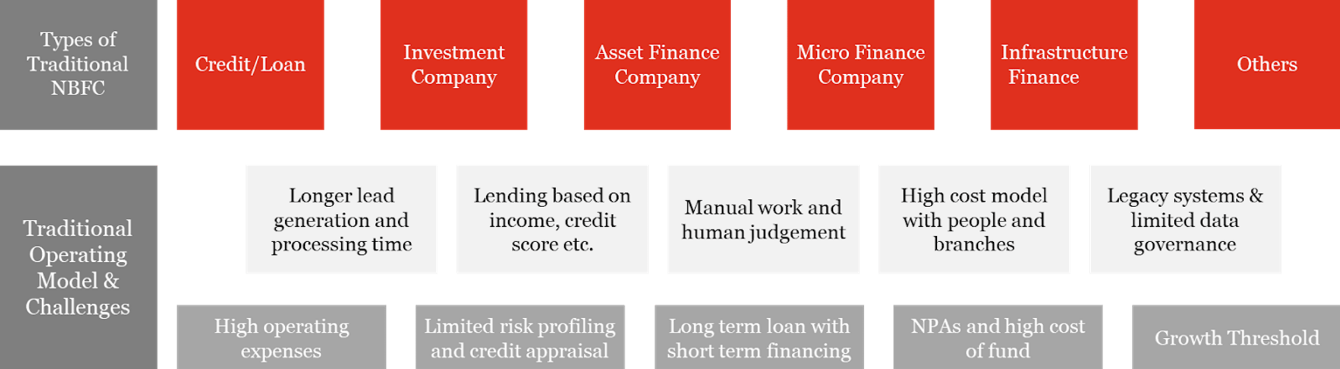
New-age NBFCs are using technology more than ever and harnessing partnership ecosystems across the value chain of lead generation, customer onboarding, underwriting, credit/loan disbursement and collection. Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML) and big data have equipped lenders to measure individual customer insights and build alternative credit scoring models. Mobile and smartphone penetration has enabled NBFCs to connect with customers having low incomes, who can use their mobiles devices throughout the lending cycle of application, engagement, e-KYC and e-signature for disbursements. Robotic process automation (RPA) has enabled streamlining of operational workflows, increasing productivity, accuracy and cost savings. NBFCs are also experimenting and beta testing with distributed ledger technologies for various use cases such as e-KYC, data exchange, loan disbursement and collection and cyber security. And application programming interfaces (APIs) are being built and tested for robust connected ecosystems of various institutions and stakeholders.
Technologies defining a new paradigm for FinTechs and NBFC
FinTechs have been creating a strong buzz across value chains in the Indian financial space. They have also become a part of the Indian government’s mission of financial inclusion for the last few years. Because of its vast potential to disrupt the current and traditional banking system, the FinTech space is now gaining traction in the areas of lending, asset management, deposits and credit system. Present-day FinTech companies are efficiently making use of new-age technologies to overcome challenges and build products and services such as last mile reach and delivery, alternative credit models, fraud detection, regulatory compliance, enterprise automation for accounting, treasury and reconciliation for traditional NBFCs.

Traditionally, lenders have adopted a ‘one size fits all’ approach, evaluating all types of customers against a single credit policy, resulting in the exclusion of a large population of creditworthy customers. With FinTechs adopting and building models on AI combined with ML and advanced analytics, NBFC lenders can adopt a personalised approach to underwriting by incorporating segment-definitive guidelines, empowered by alternative data sources, and apply scorecard-based credit decisions. The approach should help broaden the customer base, allowing sales teams to target a large pool of prospective customers and offer relevant products, as per their credit scores.
Some NBFCs are moving forward in testing and deploying solutions in collaboration with FinTech software as a service (SaaS), to automate back-end and middleware software applications, which shall make the origination and underwriting process swift, structured and transparent.
The technology-driven business model of NBFCs, which aims to reduce dependency on manual tasks and is built on the capabilities of RPA, leads to wider inclusion, cost-effectiveness, prowess in credit quality and a quicker turnaround time than traditional lending models of banks. Rather than having key resources scan pages of documentation to assess creditworthiness and risks involved in lending to an individual, technologies like RPA can enable such resources to focus on core business needs.
Technologies like AI and RPA can also aid NBFCs with on-the-spot decision making. Technologically advanced NBFCs can transform the manual, time-consuming, human judgement-based underwriting process to provide instant, real-time approvals. The transformation shall benefit NBFCs’ lenders differentiate from fellow players and traditional banks, improve customer experience, ensure uniform application of credit policies and reduce costs.
AI and ML can also help in continuous evaluation of the underwriting and risks model. A periodic re-evaluation helps determine the efficiency and effectiveness (e.g. service delivery, risk management, cost efficiency) in dynamic scenarios, and therefore, determines remediation steps to improve performance.
Advanced analytics and AI can power NBFCs with robust collections of payments and monitoring decisions. NBFCs have relied on customer account balances and credit scores to prioritise non-performing and delinquent accounts and formulate strategies for collections. But with the next level of growth slated to come from accounts with little or no credit history, NBFCs would need to leverage wider data sets and big data processing ability to derive and synthesise insights from existing and previously used data sets of non-performing or delinquent accounts, by looking at large sets of information.
Case in point
The NBFC arm of a large conglomerate was looking to scale the business, bring in innovation, create differentiation and drive real value for its stakeholders.
It is now leveraging AI, RPA and advanced analytics to create simpler processes, minimise documentation and strengthen customer delivery systems. To strengthen its position in the ecosystem, the NBFC major has built partnerships with FinTech companies specialising in AI and alternative credit scoring.
Capitalising on the surge of chatbots, the NBFC recently unveiled a first-of-its-kind voice-powered chatbot embedded within its mobile app. Powered by AI, the chatbot is designed to verbally assist a customer’s personal loan journey, from checking eligibility to approval and disbursal.
Combining shared databases and cryptography, blockchain technology allows multiple parties from varying geographical locations and not known to each other to have simultaneous access to a constantly updated digital ledger that cannot be altered.
Blockchain technology could help NBFCs by dramatically reducing onboarding and processing costs. NBFCs are keen to reduce transaction costs and the amount of paper that they process and are working in tandem with technology vendors, financial institutions and FinTechs to implement blockchain technology to make their process increasingly efficient, secure, profitable and valuable.
Case in point
A leading Indian NBFC is said to be using blockchain technology for services like travel insurance and settling claims.
To reduce fraud and improve access to credit, the ability of NBFCs to effortlessly retrieve transaction data from a borrowers’ bank account will be the foundation for future business models. With most of this data already available, it would be easier for prospective NBFCs’ lenders to get it directly from banks and other financial institutions through APIs, as against relying on intermediaries. This would make data acquisition seamless and decrease operational costs, which further can be passed on to consumers. The success of a credit risk system like this depends on the number of institutions involved and how much data is shared among them, which can be built and harnessed on frameworks of open banking and APIs.
Getting open API access to user data from consumer and business entities such as e-commerce, mobility and delivery marketplaces, telecom companies, banking and government data such as GST return filings shall allow lenders to validate the legitimacy of invoices – accounts receivables and payables, income and expense reports, receipts, purchase orders, etc., and cross-check business income from the financials. This will help NBFCs to strengthen their decision making and approve and disburse loans effectively.
Case in point
Many NBFCs, along with banks and the RBI, are working on API frameworks and policies to build an ecosystem on e-KYC and anti-money laundering (AML) to verify identities and run background and safeguard checks.
Strategic partnership models between FinTechs and NBFCs
The FinTech sector is working speedily with cutting-edge technologies, to ease borrowing for customers and solve the limitations of the banking and NBFC sectors. Banks and NBFCs are also changing their mode of operations, but at a much slower pace due to their legacy infrastructure, technologies used, frameworks, approval processes and tight-knit integration across business and technological value chains.
This does not mean that banking institutions and NBFCs are not innovating. The challenge for banks and NBFCs is to identify which ideas to actively pursue to embed capital and technology. The complexity, scale and siloed nature of banks restricts them from doing all this effectively.
Given the pace of change and customer expectations, the common trait among NBFCs is that they rightly understand that they have a better chance of succeeding by collaborating and seeking strategic partnerships with new-age FinTechs.
Traditional NBFCs have an inherent advantage which FinTech companies don’t. Similarly, FinTech companies have agility and technology, which acts as a great equaliser. We explore below the strategic partnership and innovation models adopted by banking institutions, NBFCs and FinTechs for going to market.
Environment
- In some cases, NBFCs aim to innovate internally, by building integrated solutions within their own innovation centres.
- They have been slow to innovate, given the complexity of their businesses and a strict regulatory and compliance environment
- Examples of innovation range from robo-advisors to a suite of e-lending products
Pros
- Exclusivity
- Autonomy on capital and resource allocation
- Better control on technology, talent and resources
Cons
- Challenging traditional structures and legacy systems
- Expensive to develop technology, maintain technology and hire specialists
- Lack of in-house talent
- Increased time to market
Environment
Banks enter into various types of arrangements with FinTech companies:
- Utilising products or platforms developed by FinTechs (e.g. a NBFC teaming up with a FinTech to offer alternate credit scoring, claims management or investment management services)
- Collaborating as a network to develop and test new technologies and solutions
- Referral arrangements, primarily in the lending space, where an NBFC might refer a small business that falls outside the bank’s risk appetite to a lending FinTech
- Joint ventures or co-created services (e.g. an NBFC partnering with a FinTech firm to launch a marketplace)
Pros
- Growth – acquiring new customers without significant time and resource investment
- Benefits from cutting-edge technology of FinTechs
- Addresses lack of in-house talent and innovative culture
Cons
- Finding a strategic partner and synergies
- Return on investment (ROI) of partnership
- Data security and privacy risks
- Cultural integration
- Not always an exclusive relationship
Environment
Many NBFCs have their own venture capital funds and investment funds to encourage the development of FinTech start-ups and to invest in or acquire new companies with relevant offerings
Pros
- Gains early access to innovative solutions
- Potential capital gains from early access investments through IPO or exits
Cons
- Right valuation can be challenging
- Monetisation of investment (liquidity)
Environment
Acquiring a FinTech company can increase an NBFCs’ digital footprint and act as a shortcut to development of new technology
Pros
- Rapid route into new markets
- Fast delivery/go-to market
- Exclusivity
- New customers at low cost, opportunity to cross sell products
- Access to talent and innovative culture
Cons
- Valuation
- Integration – operational, financial, technological and cultural
- Integrating new solutions into existing systems could accelerate costs
Pros
- Collaborative role with other banks/NBFCs alongside programme participants (e.g. venture capitals, government agencies, programme managers)
- Flexible to tailor staff’s level of involvement according to resource capability
- Cost shared with other parties
- Mentorship, programme sponsorship opportunities that provide enhanced FinTech network
Cons
- Limited branding opportunities
- Potentially low financial ROI if small minority stakes are shared with others
Future of NBFCs
Adopting technological innovations across value chains will aid optimisation of resources and processes, reduce turnaround time, facilitate intuitive and automated decision making and ensure accessibility of credit/loans for customers at rates tailored to their soci0economic profile. This would give NBFCs a great leverage over traditional banking systems and drive maximum possible growth. The success of NBFCs or FinTech companies is largely dependent on their ability to make the best use of technology, human capital and strategic partnerships. NBFCs have a large base of customers and FinTech companies have the right technological support; together, they can form a mutually beneficial relationship to amplify the processes of helping customers secure credit/loans.
Collaborating with FinTechs would give NBFCs the opportunity to increase revenue and provide more services without necessarily taking on additional risks or staff and while providing a more advanced customer experience. At the same time, FinTechs get access to a loyal customer base and the opportunity to maximise the experience of extensive financial services while navigating the regulatory environment.
With inputs from Avneesh Singh Narang and Raghav Aggarwal.
Contact us

Vivek Belgavi
Partner, Financial Services - Technology and FinTech Leader, PwC India
Tel: +91 22 6669 1734