5G
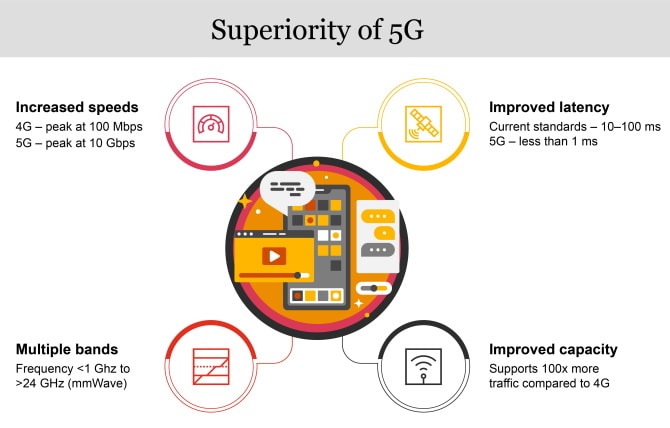
Enterprises and industries go through a myriad of aspects in order to explore and utilise the full potential of the 5G ecosystem. A tectonic shift in the business strategy and operations calls for a 5G framework that can enable enterprises understand their digital maturity. Thus, use cases, roll-out strategy and digital adoption of 5G need to be carefully assessed and gauged to derive its true value. Any vertical or industrial entity, in order to be fully 5G compliant or even have the basics ready, must weigh its potential and limitations on a standardised scale. Conceptual aspects such as cloud native, automation, edge computing and artificial intelligence (AI)/machine learning (ML) need to be evaluated from the strategic, architectural and governance aspects. Therefore, a holistic viewpoint regarding 5G adoption will help enterprises know where they stand in the 5G ecosystem.